Technical ceramics are the material of choice when traditional materials cannot meet performance requirements in thermal stability (extreme hot or cold), mechanical strength, wear resistance, hardness characteristics, chemically harsh environments, and electrical resistivity (or conductivity).
Typical Properties of Ceramics
- High hardness
- High elastic modulus
- Low ductility
- High dimensional stability
- Excellent wear resistance
- High resistance to corrosion and chemical attack
- Extreme heat resistance
- Low thermal expansion
- Good electrical insulation
- High compressive strength
Examples of how technical ceramics differ from typical steel and polymers:
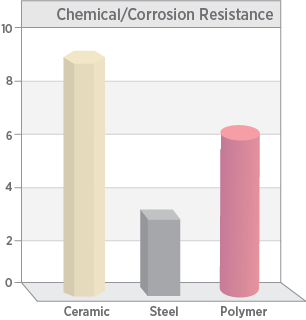
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics are well known for the resistance to chemical attack and are often specified for components used in semiconductor manufacturing, photo-voltaic manufacturing, oil & gas, chemical production, medical devices and implants, battery applications, and other highly caustic environments.
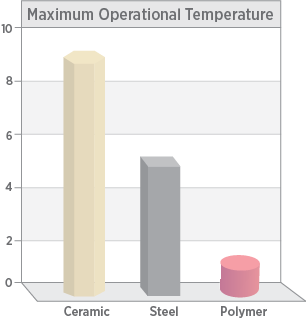
Extreme-Temperature Performance
Technical ceramics are often selected for use in extremely high and low-temperature operating environments because of their ability to retain the shape and stability over traditional materials like steel or typical polymers. Typical industrial applications include aerospace, machinery, oil & gas, automotive, and refractories.
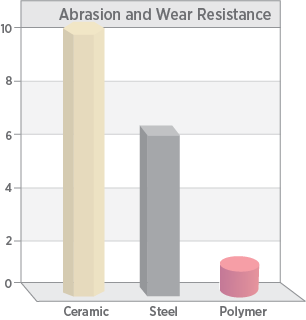
Abrasive and High-Wear Environments
Technical ceramics work very well in highly abrasive, extreme wear, or high-friction applications and outperform traditional steel and polymers/plastics.
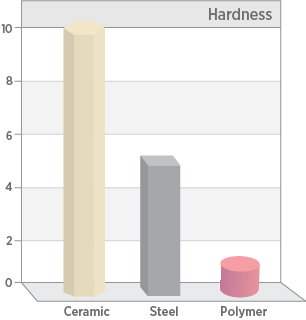
Superior Hardness
The hard technical ceramics have exceptional wear characteristics that surpass steel and polymers in heavy-duty applications and can withstand harsh environments.
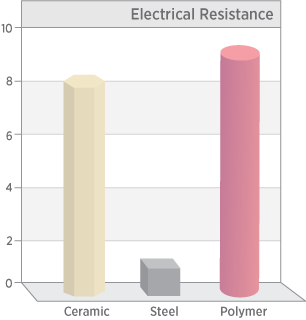
Electrical Resistivity
Technical ceramic components can be tuned to have either a high or low resistivity while polymers are highly electrically insulating. Typically, ceramics have extremely low electrical conductivity and high dielectric strength which make them ideal for electrical insulators.
For more information, visit The American Ceramic Society page describing ceramics and glass.
To learn more about how technical ceramics can enhance performance for your engineering challenge, please contact us.

